Home > Climate News >

New forest carbon offset strategies turn to small landowners for big impact
This article highlights two programs with innovative methods for lowering the barriers to participation, combining small individual parcels into landscape-level carbon storage.
While Silviaterra leverages GIS data toward lower monitoring costs, the Family Forest Carbon Program focuses on incentivizing specific management practices based on estimated climate benefits.

Personal stories can shift climate change beliefs and risk perceptions: the mediating role of emotion
Using two experiments, a group of researchers test the effects of a radio story on the climate change beliefs and risk perceptions of political moderates and conservatives.
The radio story, which aired on hundreds of stations across the U.S., is a North Carolina sportsman’s personal account of how climate change has already affected the places he loves. Both experiments found positive effects on global warming beliefs and risk perceptions. Additionally, Study 2 found these effects were mediated by emotional reactions of worry and compassion. These studies suggest personal stories can be a persuasive communication strategy…

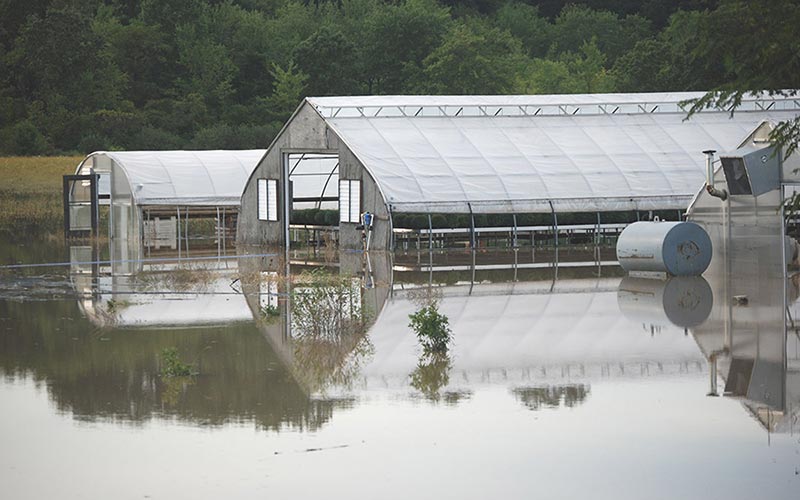
Daphne Prairie and other Texas grasslands can store carbon and help fight climate change
Scientists say the world needs to cut greenhouse gas emissions nearly in half by mid-century to avert catastrophic effects from global warming. Carbon dioxide is the most prevalent greenhouse gas; the amount in the atmosphere has been rising as humans burn fossil fuels. Not only must the world stop releasing more carbon, some CO2 already in the air also must be removed, experts say…

New England’s forests are sick. They need more tree doctors.
To spend time with tree experts is to remove one’s green-tinted glasses and to see Oz as it really is. Many species—including ash, oak, maple, hemlock, elm, and white pine—have their own particular pest or disease threatening them. And there are more pests and diseases on the horizon, including insects like the spotted lantern fly and infections that weakened trees cannot fight off.
Many trees are also stressed by bouts of drought or intense rain; by rising temperatures and changing season length; by extreme weather; by all the various manifestations of climate change…

Just how does solar grazing work?
There can be concerns about solar overtaking farmland. Yet with good design and partnership with farmers, solar can actually improve soil health and keep farmers on the land. Here’s a short video by Owens Farm, in Pennsylvania, about how solar grazing works.
For additional information, including leases and technical documents, check out American Solar Grazing Association.

On-farm solar grows as farmers see economic rewards—and risks
Steve Pierson switched from raising conventional dairy cows in confinement to grazing the animals on organic pasture for a simple reason: they kept getting sick. He had heard and read about the fact that cows that ate grass had healthier immune systems, since their bodies are designed to digest grasses, not the grain used as feed at most dairies. The transition did make the cows live longer, and he also began to notice other environmental benefits, such as healthier soil and more perennial grasses…
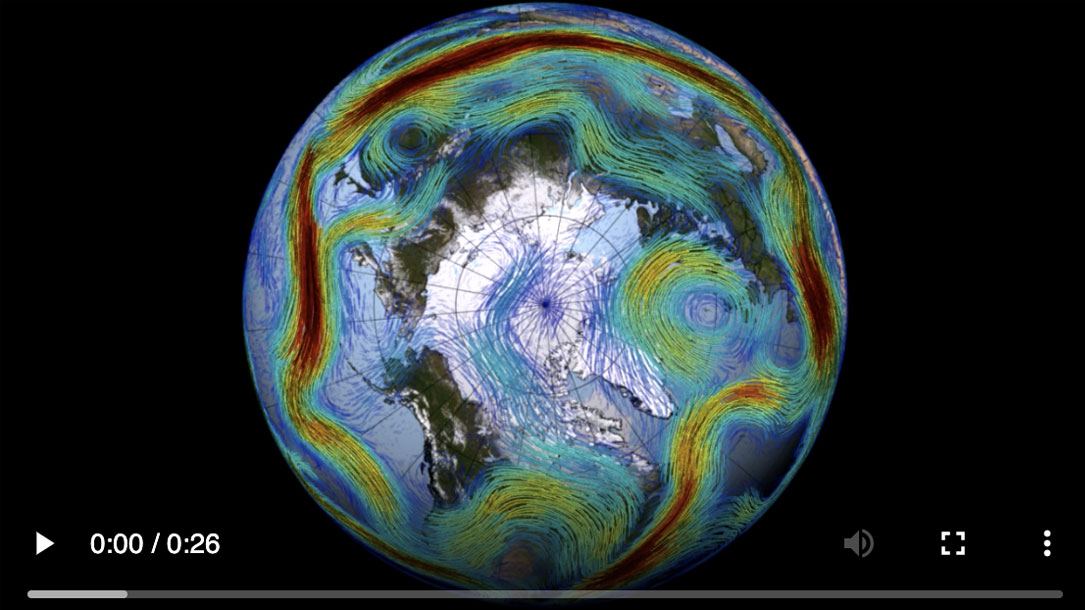
Polar Vortex: how the jet stream and climate change bring on cold snaps
The jet stream—a powerful river of wind high in the atmosphere—shapes the Northern Hemisphere’s weather, including bitter cold snaps. Because it plays a key role in weather extremes, climate scientists are striving to understand its changing dynamics.
Here’s a closer look at what the jet stream is, what’s influencing its wobbly behavior and why it matters…

2020 is on course to be the warmest year on record
While this year will be memorable for many reasons, it is now more likely than not that 2020 will also be the warmest year for the Earth’s surface since reliable records began in the mid-1800s.
This is all the more remarkable because it will lack any major El Niño event – a factor that has contributed to most prior record warm years…

A new marketplace for carbon capture
Hudson Carbon is an on-farm soil laboratory. We study how organic regenerative farming can maximize carbon capture and restore ecosystems.
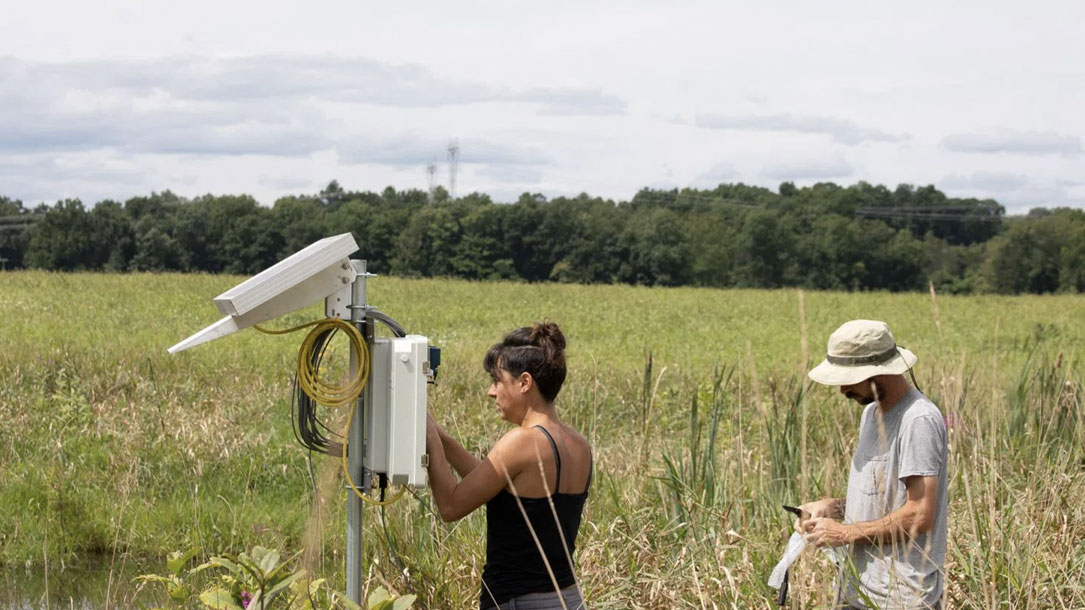

Farmers on the front lines of climate change
Housed at Stone House Farm in Columbia County, NY, Hudson Carbon is emerging as one of the most ambitious testing grounds for carbon farming in the country. Soon to launch an e-commerce carbon offset market—with Stone House as its pilot—Hudson Carbon’s ultimate goal is to enable regional farmers to receive just compensation, not only for carbon sequestration practices, but for a full range of ecosystem services.
It employed a set of complementary regenerative agriculture practices with the goals of reducing tillage; maximizing soil cover to enhance photosynthesis; increasing beneficial insects, plant, and microbial biodiversity; improving nutrient cycling; increasing water efficiency and infiltration; integrating pastured animals; and increasing carbon stock above the soil level through agroforestry techniques…












