Fish Deaths in Montana’s Yellowstone River Tied to Warming Waters
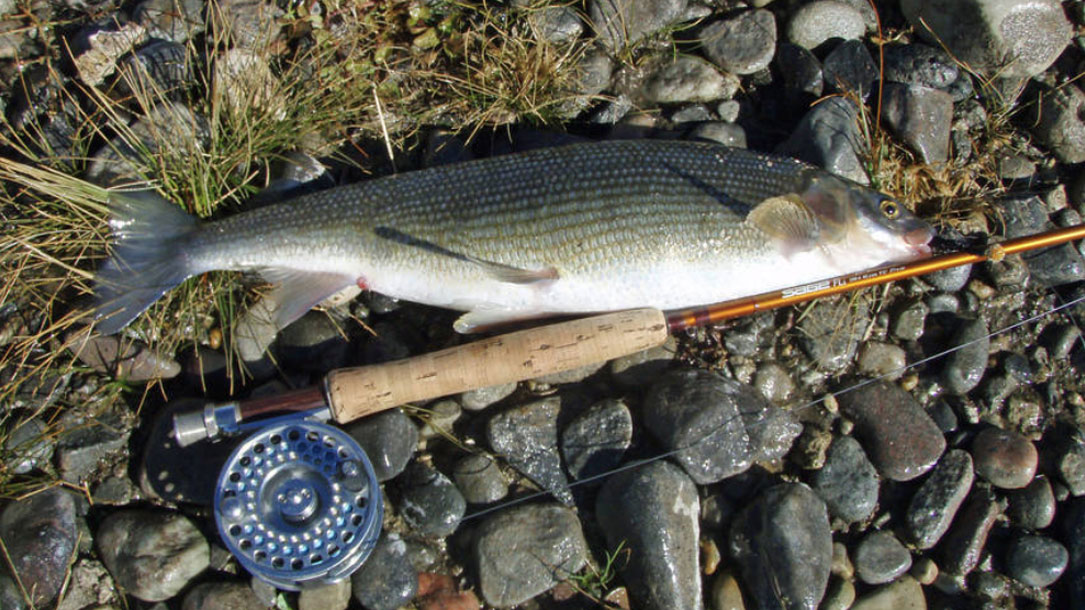
“An outbreak of fish-killing disease along a 100-mile stretch of the Yellowstone River in Montana may be the latest sign that mountain stream ecosystems are being disrupted by climate change. Scientists point to warmer, slower rivers as a likely cause of the mass fish mortality.
Since Aug. 12, the Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks has counted 4,000 dead mountain whitefish, along with smaller numbers of rainbow trout, Yellowstone cutthroat, longnose suckers, sculpin and longnose dace. The agency estimate that tens of thousands of fish may be dead and they closed the segment to recreation to reduce impacts to fish. This is happening along a river that’s an economic mainstay for nearby communities and thought of as a relatively healthy, undammed river…”

Crop pests and pathogens move polewards in a warming world
“Global food security is threatened by the emergence and spread of crop pests and pathogens. Spread is facilitated primarily by human transportation, but there is increasing concern that climate change allows establishment in hitherto unsuitable regions. However, interactions between climate change, crops and pests are complex, and the extent to which crop pests and pathogens have altered their latitudinal ranges in response to global warming is largely unknown…”
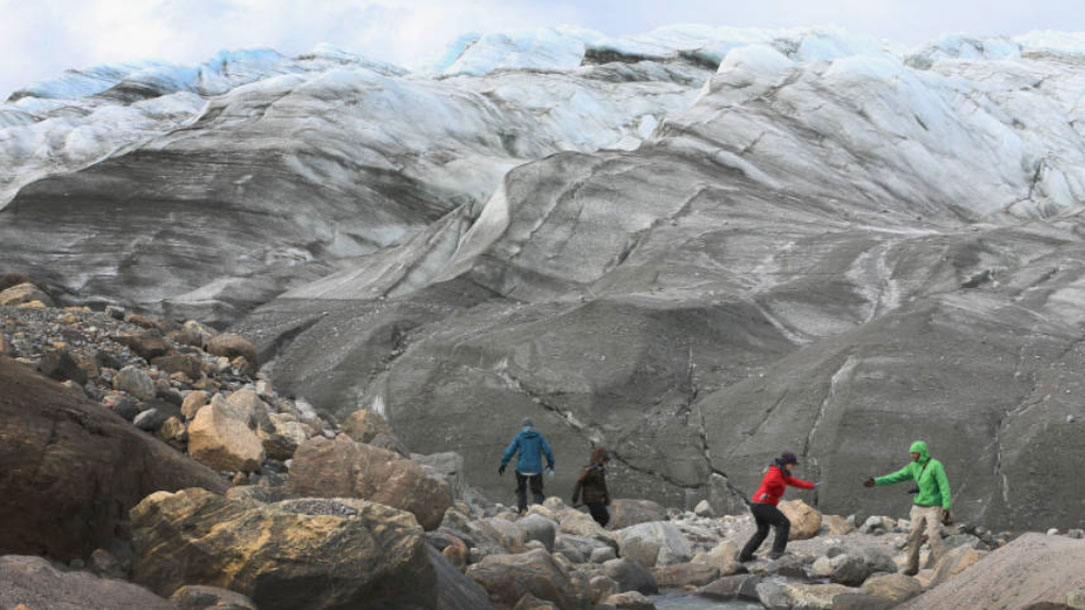

What’s Eating Away at the Greenland Ice Sheet?
“In the high-stakes race against sea level rise, understanding what’s causing the Greenland Ice Sheet to melt is critical. The problem isn’t just rising temperatures: soot from ships, wildfires and distant power plants, as well as dust and a living carpet of microbes on the surface of the ice, are all speeding up the melting.
Right now, predictions for sea level rise range from about 1 to 10 feet by 2100—a wide difference for coastal communities trying to plan seawalls and other protective measures…”
Global warming pushes microbes into damaging climate feedback loops
“[G]lobal warming is supercharging some microbial cycles on a scale big enough to trigger damaging climate feedback loops, research is showing. Bacteria are feasting on more organic material and producing extra carbon dioxide as the planet warms. In the Arctic, a spreading carpet of algae is soaking up more of the sun’s summer rays, speeding melting of the ice.
Deadly pathogenic microbes are also spreading poleward and upward in elevation, killing people, cattle, and crops…
Research has shown that accelerated microbial activity in soils will significantly increase carbon emissions by 2050. In another study, global warming favors fungi that quickly break down dead wood and leaves and release CO2 to the atmosphere.
Other warning signs from the microbial world include spreading crop diseases that threaten food security, microbial parasites that threaten freshwater fish, as well as the fungal epidemic wiping out amphibians world wide…

Nature’s dangerous decline ‘unprecedented’; species extinction rates ‘accelerating’
“Nature is declining globally at rates unprecedented in human history — and the rate of species extinctions is accelerating, with grave impacts on people around the world now likely, warns a landmark new report from the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), the summary of which was approved at the 7th session of the IPBES Plenary, meeting last week (29 April – 4 May) in Paris…”

Why Solar Power Is Good for Birds
“If you install solar panels on your roof, don’t expect your birds to show any appreciation. At best, they’ll bless them with a splatter of droppings. But if they knew better, they’d be grateful, because installing solar panels at home is one of the best ways to help birds avoid the worst impacts of climate change…”

Climate Change and Moose: Moose are like canaries in the coal mine
While capturing 179 moose calves and attaching radio collars to them, researchers counted an average of 47,371 ticks on each animal, with a high count of more than 96,000.
Since each adult female tick can suck up to three milliliters of blood from its host, Pekins said the high number of ticks could drain the blood of a moose calf in two to three weeks. As a result, in four out of the five years of the study, at least half of all moose calves that researchers were following died; in New Hampshire and western Maine, the mortality rate was 70 percent…
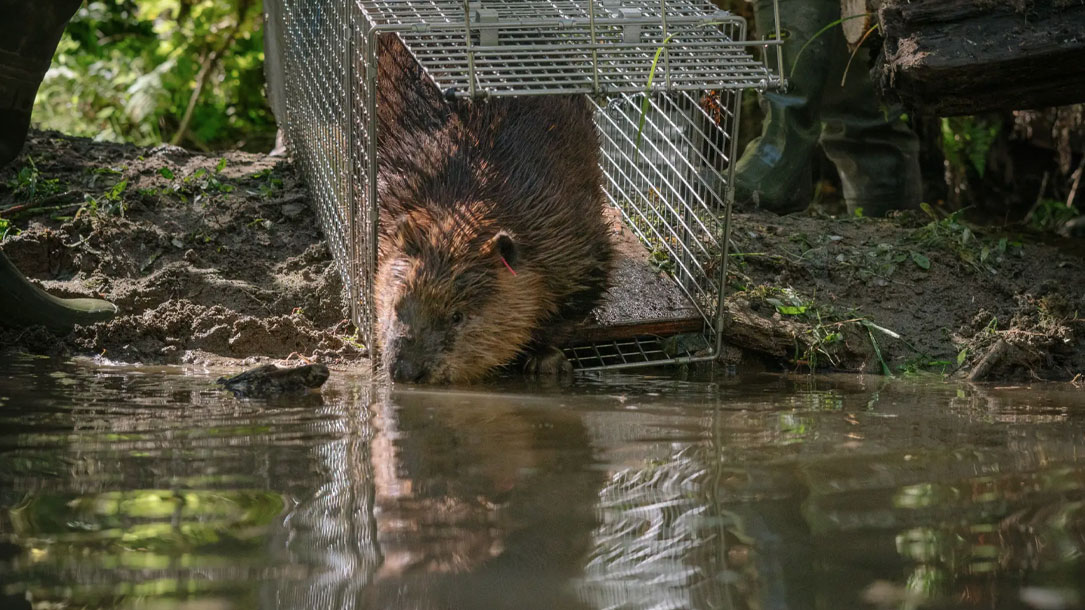

An indigenous tribe in Washington is strategically placing beavers around to help salmon
The sentiment that Castor canadensis is little more than a tree-felling, water-stealing, property-flooding pest is a common one. In 2017, trappers in Washington State killed 1,700 “nuisance” beavers, nearly 20 times more than were relocated alive. In neighboring Oregon, the herbivorous rodents are classified as predators, logic and biology notwithstanding. California considers them a “detrimental species.” Last year alone, the U.S. Department of Agriculture eliminated more than 23,000 conflict-causing beavers nationwide.
Running countercurrent to this carnage is another trend: the rise of the Beaver Believer. Across North America, many scientists and land managers are discovering that, far from being forces of destruction, beavers can serve as agents of water conservation, habitat creation, and stream restoration…
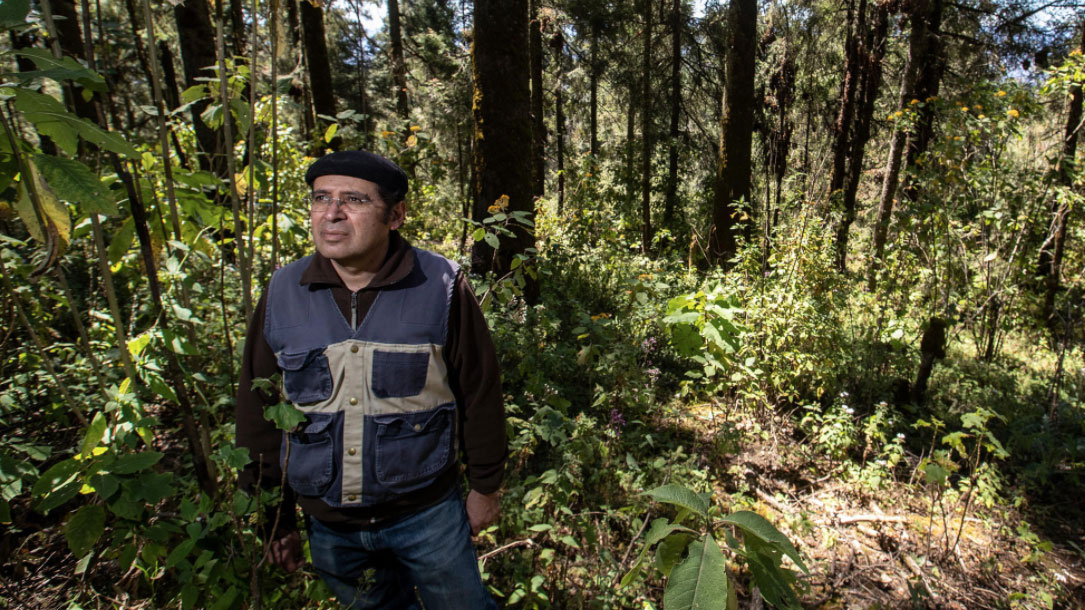

To save the monarch butterfly, Mexican scientists are moving a forest 1,000 feet up a mountain
The world is losing monarch butterflies at a startling rate, as logging, herbicides, and other human activities destroy natural habitats. But the biggest threat yet has only recently come into focus. Climate change, with its extreme storms, prolonged droughts, and warming temperatures, is poised to eradicate the forest that serves as the butterfly’s winter refuge.
To help his beloved butterflies, Ramirez has partnered with scientists on a monumental experiment: They are trying to move an entire forest 1,000 feet up a mountain…

Climate change is leading to unpredictable ecosystem disruption for migratory birds
“Climates have natural variation and we’re moving rapidly into territory where the magnitude of climate change will consistently exceed this variation,” says lead author and Cornell Lab researcher Frank La Sorte.
“There will be no historic precedent for these new climates, and migratory bird populations will increasingly encounter ‘novel’ climatic conditions. The most likely outcome will be a period of ecological disruption as migratory birds and other species try to respond or adapt to these new conditions…”












