Alley cropping case studies in Appalachia
The Natural Resource Conservation Service (NRCS) describes alley cropping as having several conservation purposes, including reducing surface water runoff and erosion, improving soil health, altering subsurface water quantity or water table depths, enhancing wildlife and beneficial insect habitat, increasing crop diversity, and increasing carbon storage.
Much like agrivoltaics with crops and/or cattle, the combined farming practice can increase overall yields and benefits. Plus, funding may be available. The case study focuses on Appalachia but could be emulated elsewhere.
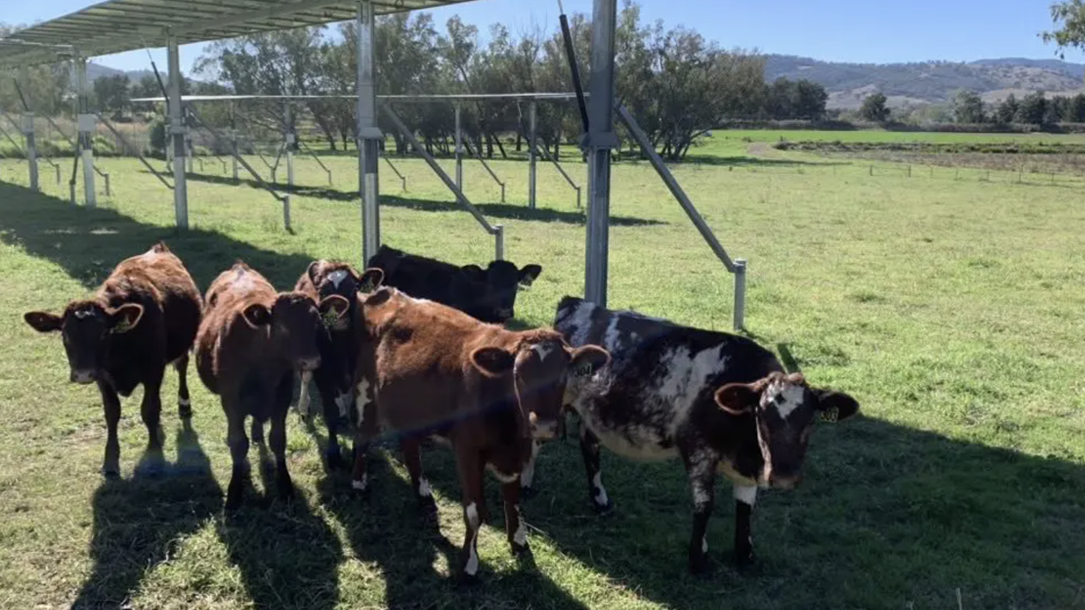

Solar farms put cow comfort and crop yield ahead of harvesting electrons
Solar arrays that promise to generate happier, healthier cows and crops, while producing cheap electrons on the side, are being put into practice in France, following a series of government-led energy tenders with a difference…
To really drive home this focus, the French government used contracts for the difference where the price per MWh is set for 20 years above the market value to compensate for the prioritization of agriculture and livestock over maximum solar production…

New York City’s greenery absorbs a surprising amount of its carbon emissions
A study of vegetation across New York City and some densely populated adjoining areas has found that on many summer days, photosynthesis by trees and grasses absorbs all the carbon emissions produced by cars, trucks and buses, and then some. The surprising result, based on new hyper-local vegetation maps, points to the underappreciated importance of urban greenery in the carbon cycle…
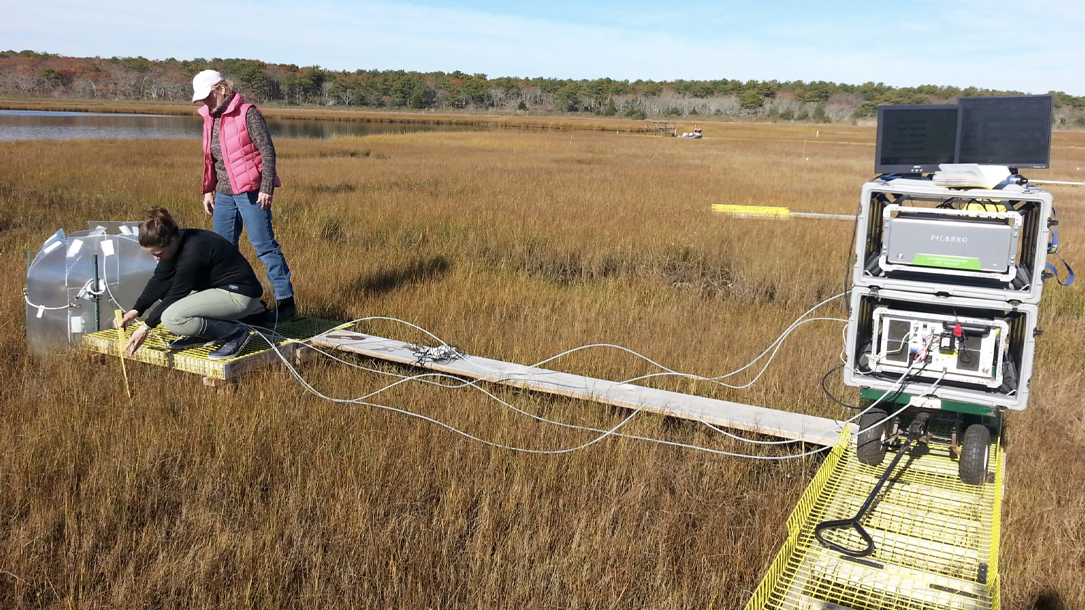

Low salt marsh habitats release more carbon in response to warming, a new study finds
Salt marshes, excellent reservoirs of carbon, are living ecosystems with vegetation and microscopic organisms that live, breathe, poop, and die in the marsh mud.
“This is a place where you could get the biggest bang for your buck, if you will, if you’re interested in trying to invest some resources in sequestering carbon using biological systems,” said Serena Moseman-Valtierra, an associate professor of biological science at the University of Rhode Island.
Yet as temperatures rise, marshes at the lowest elevations may also be significant emitters of carbon…

Scientists sound alarm as ocean temperatures hit new record
The world’s oceans, which have absorbed most of the excess heat caused by humanity’s carbon pollution, continued to see record-breaking temperatures last year, according to research published Wednesday.
Climate change has increased surface temperatures across the planet, leading to atmospheric instability and amplifying extreme weather events such as storms…
Farmer first solar: Agrivoltaics webinar series
The AgriSolar Clearinghouse is an information-sharing, relationship-building public communications hub for all things agrisolar. The AgriSolar Clearinghouse is offering a free series of webinars regarding research on how solar and agriculture can work (and are working) together to enhance farm/ranch viability, soil health, and water management.
Webinar topics include: the cost of agrivoltaics, growing crops under solar panels, taste differences among crops grown under panels, solar and pollinator habitats, and more. You can sign up here, or watch recordings of past webinars.

Climate change, habitat loss (and, yes, even cats) pose a greater threat to birds than windmills
Research quantifying the full scale of wind turbine activity’s impact upon birds both through their migratory patterns and killed by collision with wind turbines is a matter of current scientific studies. It is important to quantify these impacts, but it is also important to acknowledge that these impacts are certainly negligible compared to other drivers of bird mortality.
The number of birds killed by wind turbine collisions per year is estimated to be between 150,000 and 500,000, but when you put this number in perspective, it pales in comparison to other causes of bird mortality…

Solar panels help French winemaker keep climate change at bay
A roof of solar panels shades Pierre Escudie as he inspects the last plump grapes to be harvested at his vineyard in southwest France, after a year of hard frosts and blistering heat that damaged many of his neighbors’ crops.
The solar panels insulate the grapes during periods of extreme cold and shield them from the sun’s harsh rays during heat waves. The panels also rotate to allow more light to hit the vines on more overcast days…

Ancient grasslands guide ambitious goals in grassland restoration
Grasslands, which constitute almost 40% of the terrestrial biosphere, provide habitat for a great diversity of animals and plants and contribute to the livelihoods of more than 1 billion people worldwide. Whereas the destruction and degradation of grasslands can occur rapidly, recent work indicates that complete recovery of biodiversity and essential functions occurs slowly or not at all. Grassland restoration—interventions to speed or guide this recovery—has received less attention than restoration of forested ecosystems, often due to the prevailing assumption that grasslands are recently formed habitats that can reassemble quickly. Viewing grassland restoration as long-term assembly toward old-growth endpoints, with appreciation of feedbacks and threshold shifts, will be crucial for recognizing when and how restoration can guide recovery of this globally important ecosystem.

Oft-overlooked grasslands build biodiversity, resilience over centuries
Grasslands’ biodiversity and resilience to disturbances such as fire, heat, and drought is the result of a slow process over hundreds of years, like that of old-growth forests, finds new CU Boulder-led research.
Published in the journal Science on August 5, 2022 as part of a special issue on grasslands, the study contradicts years of assumptions that grasslands’ ecological development is quick and their recovery is rapid, posing new challenges to their successful restoration.
“Old-growth grasslands have a unique suite of characteristics that develop over a really long time…”












