Home > Climate News >
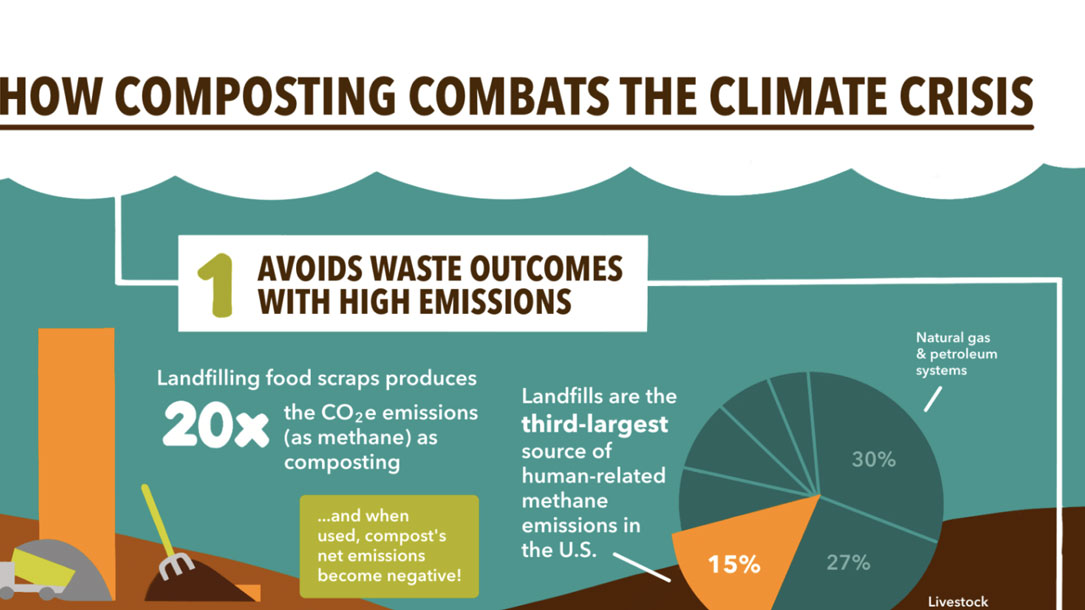
Infographic: How composting combats the climate crisis
Composting cuts greenhouse gas emissions, enhances the ability of soil to act as a carbon sink, and builds community resilience to climate disruptions.
Use our new graphic to share these benefits! It is available for your use (with attribution to the Institute for Local Self-Reliance).

Deep soil inventories reveal that impacts of cover crops and compost on soil carbon sequestration differ in surface and subsurface soils
Increasing soil organic carbon (SOC) via organic inputs is a key strategy for increasing long-term soil C storage and improving the climate change mitigation and adaptation potential of agricultural systems. A long-term trial in California’s Mediterranean climate revealed impacts of management on SOC in maize-tomato and wheat–fallow cropping systems. SOC was measured at the initiation of the experiment and at year 19, at five depth increments down to 2 m, taking into account changes in bulk density. Across the entire 2 m profile, SOC in the wheat–fallow systems did not change with the addition of N fertilizer, winter cover crops (WCC), or irrigation alone and decreased by 5.6% with no inputs.

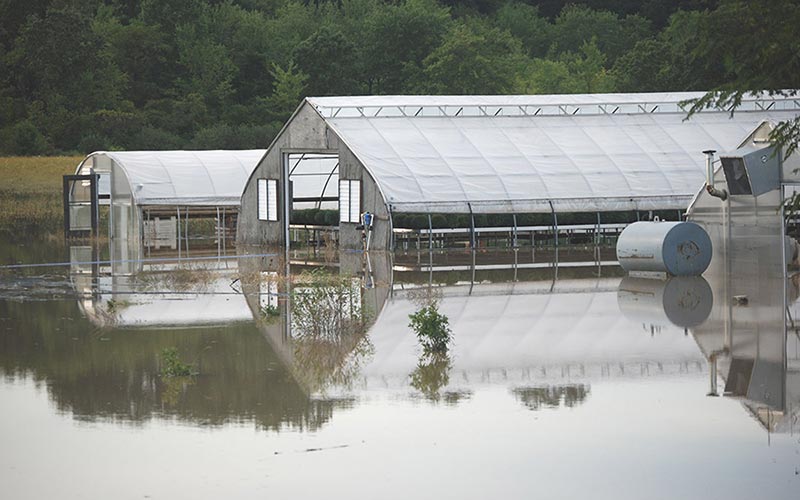
One simple way to slash methane pollution: composting
In the United States, a staggering one-third of all food — something like 130 billion meals annually — gets thrown out. Each year, that discarded stuff represents an estimated 170 million metric tons of carbon emissions — the equivalent of 42 coal-fired power plants…
According to a new study in the Nature Journal Scientific Reports, composting food scraps results in 38 to 84 percent fewer greenhouse gas emissions than tossing them in landfills…

New research shows practices from the past will be key to future soil carbon solutions
Sometimes to go forward, you must go back.
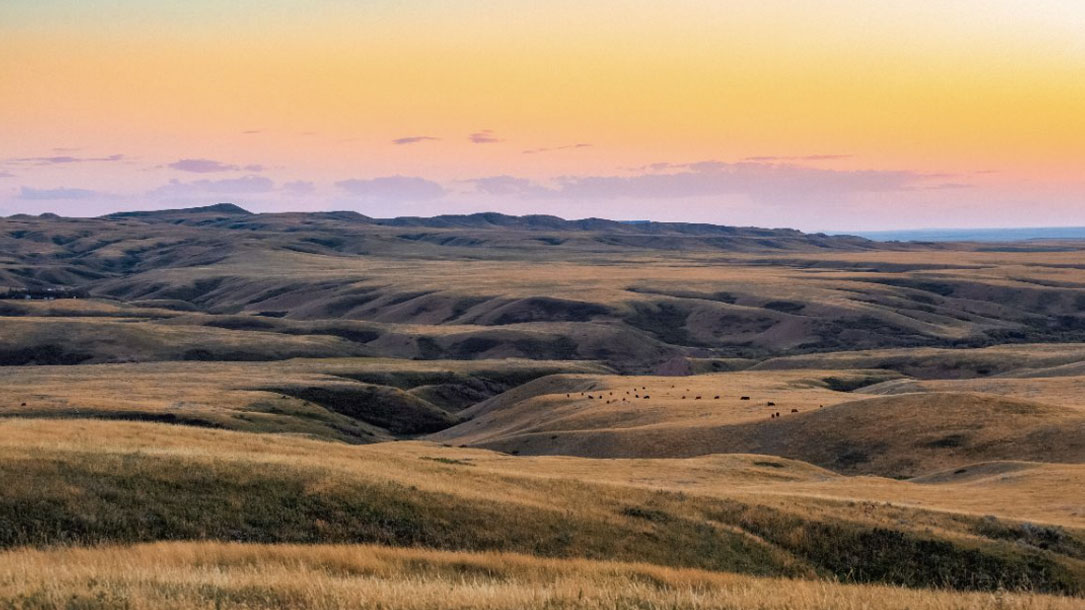
A new study from Colorado State University’s Department of Soil and Crop Sciences and the Graduate Degree Program in Ecology found that regenerative practices — including integrating crop and livestock systems — were successful as long-term carbon storage solutions.

Regenerative practices successful at long-term carbon storage, study finds
A meta-analysis conducted by Colorado State University researchers found that regenerative agricultural practices are successful as long-term carbon storage solutions. The research considered two different types of soil carbon, particulate organic carbon (POC) and mineral-associated organic carbon (MAOC). Because POC cycles faster in soil, different management for the two types of carbon may help provide better outcomes…

NSAC’s 2023 Farm Bill Platform
NSAC’s comprehensive 2023 Farm Bill Platform provides title-by-title recommendations across farm bill programs and policies detailing how Congress can better support farmers and ranchers by strengthening their bottom lines, their communities, and their resilience. The platform spans key issue areas including natural resource conservation, local and regional food systems, sustainable agriculture research, structural reform to farm programs, and more, with cross-cutting recommendations, focused on advancing racial equity across farm bill programs, supporting beginning farmers, and addressing the climate crisis and its impacts on our food and farms.
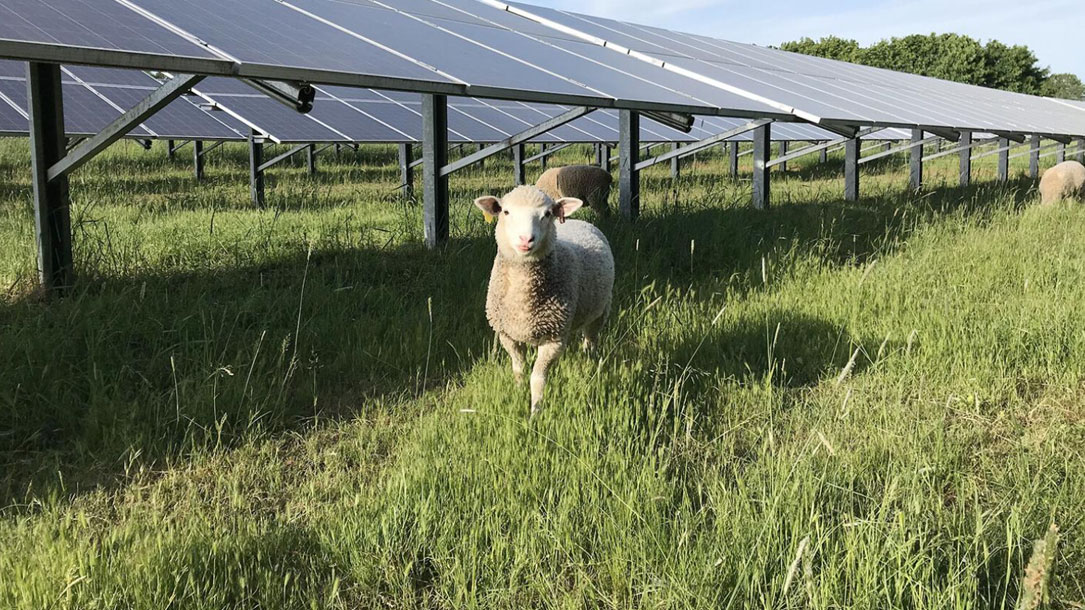

Agrivoltaics bill introduced in U.S. Senate
According to the National Sustainable Agriculture Coalition (NSAC), the study would aim to answer many questions about agrivoltaics, including what panel designs are best for livestock versus crops; what animal breeds are best suited to graze under panels; how to handle fencing, manure, and other livestock considerations in solar panel systems; and how growing crops under panels impacts yields, soil moisture, and other factors.

Climate-smart agriculture Inflation Reduction Act Activation Guide
A broad range of companies within the food sector can use IRA-funded agricultural programs to support their climate goals. On average, two-thirds of food sector companies’ emissions are generated by farm-level production, making on-farm sustainability critical for abatement.

Climate change, antibiotics may threaten soil
A study by researchers at the Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies in Millbrook, New York, has shown that when rising temperatures combine with antibiotic residues expelled by livestock, it degrades soil microbe efficiency, soil resilience to future stress, and its ability to trap carbon…
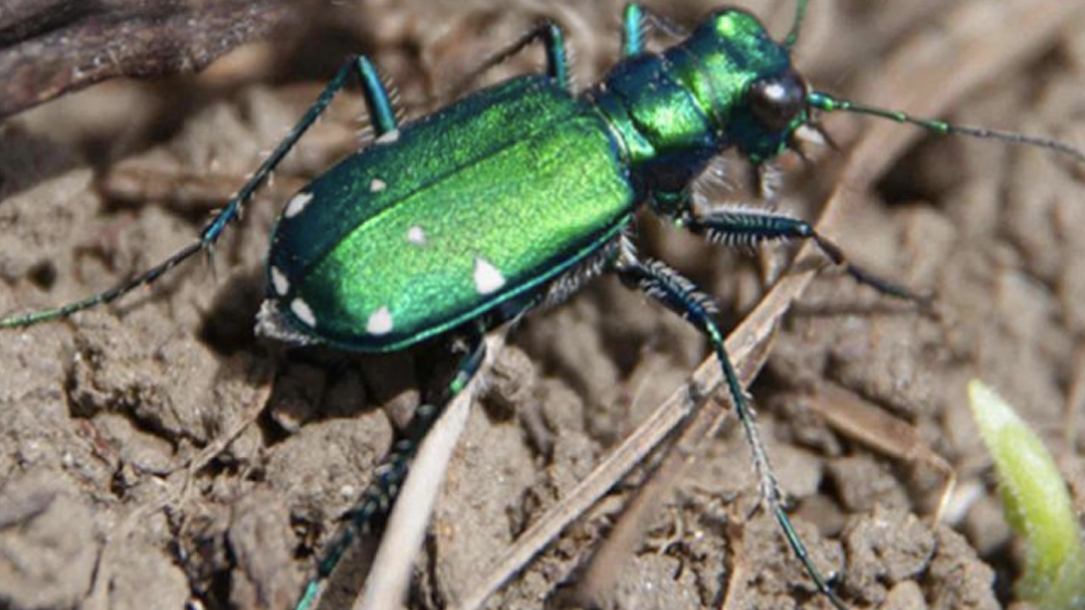

Future of many North American crops may depend on ground beetles’ response to climate change
By analyzing data on 136 different ground beetle species from diverse habitats across continental North America, Puerto Rico and Hawaii, the researchers found that a species’ odds of success in a changing climate depend on several core traits, such as its habitat preference, body size, and whether it flies, burrows, climbs, or runs.
“We found that less mobile, nonflying ground beetles, which are critical pest control agents, are more likely to decline over time in a warmer, dryer climate,” said Tong Qiu, assistant professor of multifunctional landscapes at Penn State, who led the study. “That means you’re going to have more pests that can impact agricultural and forest ecosystems…”












