Home >

Carbon farming
Agriculture is part of the climate solution. Grasslands are one of the largest carbon sinks on the planet, capable of pulling enormous quantities of CO2 from the atmosphere and storing it in the soil.
Carbon farming is the process of farming and ranching to maximize the land’s ability to lock up CO2 and other greenhouse gases, making the land more resilient to the effects of a changing climate.
Marin Agricultural Land Trust (MALT) partners with MALT farmers and ranchers to implement carbon farming practices, benefiting farmers, their land, and the climate…

Land trusts ink deal to conserve 20 acres along Mill River in Williamsburg
Mark Wamsely, [Kestrel Land Trust’s] conservation director, highlighted the conservation as a way to combat climate change. The [press] release also notes the state’s 2022 Climate Change Assessment, which states that risk of flooding and erosion in the hilltowns is likely over the coming century.
“It’s important that we address climate change in a thoughtful way and don’t accidentally harm the very natural resources that are under threat,” said Wamsley, adding that, “Conserving forests is one way the Hilltowns can make a critical contribution to combating climate change.”

Climate change website pages
Land trusts often wonder how they can increase their efforts to connect with people around climate change, meet them where they are, and inspire local, regional, and national action.
Many land trusts start with nature-based climate solutions as a way to connect. However, it’s important for people to also understand what they can do as individuals based upon their interests and capacity, in addition to what the land trust is doing.
If you are interested in enhancing climate messaging or raising the profile of your local land trust, you might find the Coastal Prairie Conservancy’s climate pages of interest.

Mississippi Valley Conservancy planting trees to help combat climate change
Carol Abrahamzon, Executive Director of the Mississippi Valley Conservancy, met with the local TV station to talk briefly about a restoration project they are working on.
“Abrahamzon says these trees are essential to providing a healthy habitat to the Coulee Region. The trees to be planted at the Conservancy’s Trempealeau Lakes nature preserve include swamp white oak, silver maple, and river birch.
Abrahamzon says that the selected tree species are native to the Driftless Area and will adapt well to this site and require little care after they become established. All of these benefits strengthen the land’s resilience to a changing climate…”

Watch Greta Thunberg’s full talk
“When I was about eight years old, I first heard about something called ‘climate change.’ I remember thinking that it was very strange. If burning fossil fuels was so bad that it threatened our very existence, how could we just continue like before. So, why are we not reducing our emissions?”

Yale experts explain climate anxiety
“Every day, the news delivers fresh images and headlines about climate-related disasters — devasting floods, disappearing lakes, a melting ‘doomsday glacier’—and the halting response of world leaders to act with urgency. Now many Americans are growing increasingly anxious about the perilous state of our planet.
Mental health clinicians are seeing more patients come in with symptoms of climate change anxiety—also referred to as eco-anxiety, eco-grief, or climate doom—and they’re not always sure what to do about it. It’s a trend that’s mirrored in public surveys and internet search data: Google searches for “climate anxiety” soared by 565 percent in 2021, according to the news outlet Grist…”

New research shows global climate benefits of protecting nature, but it’s not a silver bullet
Since 2000, the researchers reported, protected forests worldwide have stored 9.65 billion metric tons more carbon in their trunks, branches, and stems than ecologically similar unprotected areas. That is equal to about a year’s worth of annual carbon dioxide emissions from human activities. But that doesn’t mean that nature is a silver bullet that will stop climate change, said lead author Laura Duncanson, an assistant professor and remote sensing scientist at the University of Maryland who studies global carbon stocks.
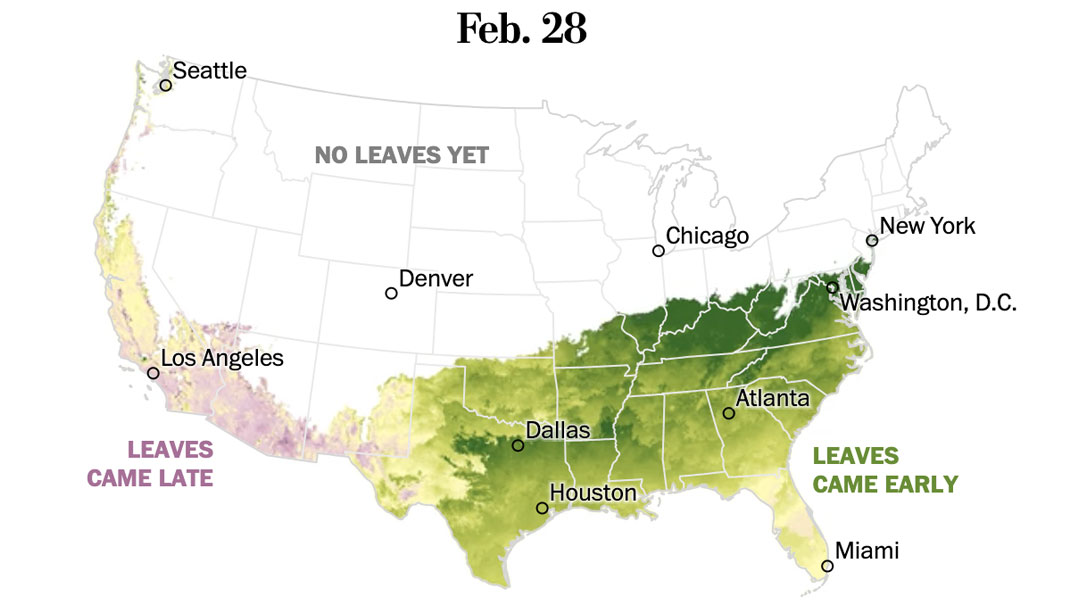
When will spring come? Or has it already? Look up where you live.
All across the east, naturalists are exasperated. As the rest of us luxuriated in this winter’s uncommon mildness, gardeners and wildlife biologists watched with rising pique as one of the earliest springs in recent memory threw nature’s rhythms out of whack.
Ignorant of the human calendar, nature instead responds to the gradual accumulation of heat at the beginning of each year. If the daily average temperature is above freezing, that sends a signal to plants and animals that life is again preparing to grow. Each year, the USA National Phenology Network — phenology is the study of seasonal change — keeps track of when leaves sprout as heat accumulates across the country.

Trees are moving north from global warming. Look up how your city [region] could change.
As the climate warms, horticulturalists are trying out species adapted to more southern climates. Michael Hagen, curator of the native plant and rock gardens at the New York Botanical Garden, told me recently that his colleagues are planting southern live oaks, known for the Spanish moss that drapes, ghostlike, from their limbs.
Live oaks can grow as far north as Zone 7, according to data provided by the Davey Tree Expert Company. By century’s end, they could grow in Chicago and up into Michigan, while south Florida could become too hot for them.

Assessing the climate change mitigation potential from food waste composting
Food waste is a dominant organic constituent of landfills, and a large global source of greenhouse gases. Composting food waste presents a potential opportunity for emissions reduction, but data on whole pile, commercial-scale emissions and the associated biogeochemical drivers are lacking. We used a non-invasive micrometeorological mass balance approach optimized for three-dimensional commercial-scale windrow compost piles to measure methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions continuously during food waste composting. Greenhouse gas flux measurements were complemented with continuous oxygen (O2) and temperature sensors and intensive sampling for biogeochemical processes.












