Home >

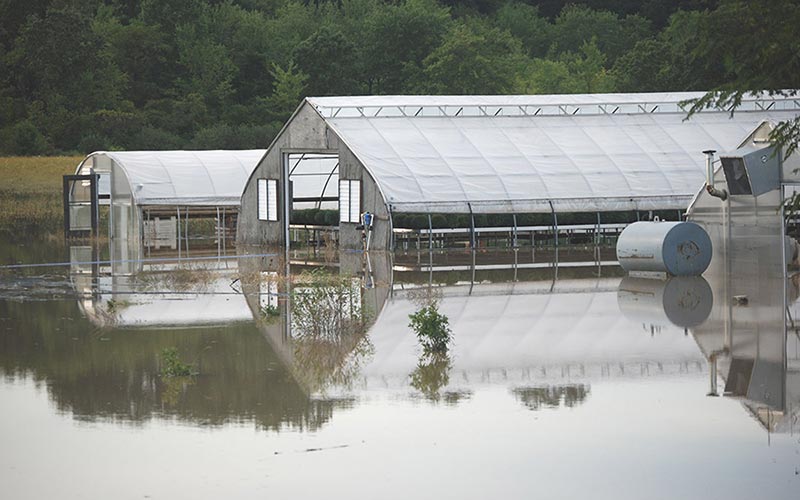
From farm to kitchen: The environmental impacts of U.S. food waste
Over one-third of the food produced in the United States is never eaten, wasting the resources used to produce it and creating a myriad of environmental impacts. Food waste is the single most common material landfilled and incinerated in the United States, comprising 24 and 22 percent of landfilled and combusted municipal solid waste, respectively. This wasted food presents opportunities to increase food security, foster productivity and economic efficiency, promote resource and energy conservation, and address climate change.
As the United States strives to meet the Paris Agreement targets to limit the increase in global temperature to 1.5 degrees above pre-industrial levels, changes to the food system are essential. Even if fossil fuel emissions were halted, current trends in the food system would prevent the achievement of this goal. Globally, food loss and waste represent 8 percent of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions (4.4 gigatons CO2e annually), offering an opportunity for meaningful reductions.

How much food waste is there in the United States?
Each year, 119 billion pounds of food is wasted in the United States. That equates to 130 billion meals and more than $408 billion in food thrown away each year. Shockingly, nearly 40% of all food in America is wasted.
Food goes to waste at every stage of food production and distribution – from farmers to packers and shippers, from manufacturers to retailers to our homes. Food waste in our homes makes up about 39% of all food waste – about 42 billion pounds of food waste. While commercial food waste makes up about 61% of all food waste or 66 billion pounds of food waste. Feeding America focuses on reducing food waste on farms and in food service, manufacturing, and retail.
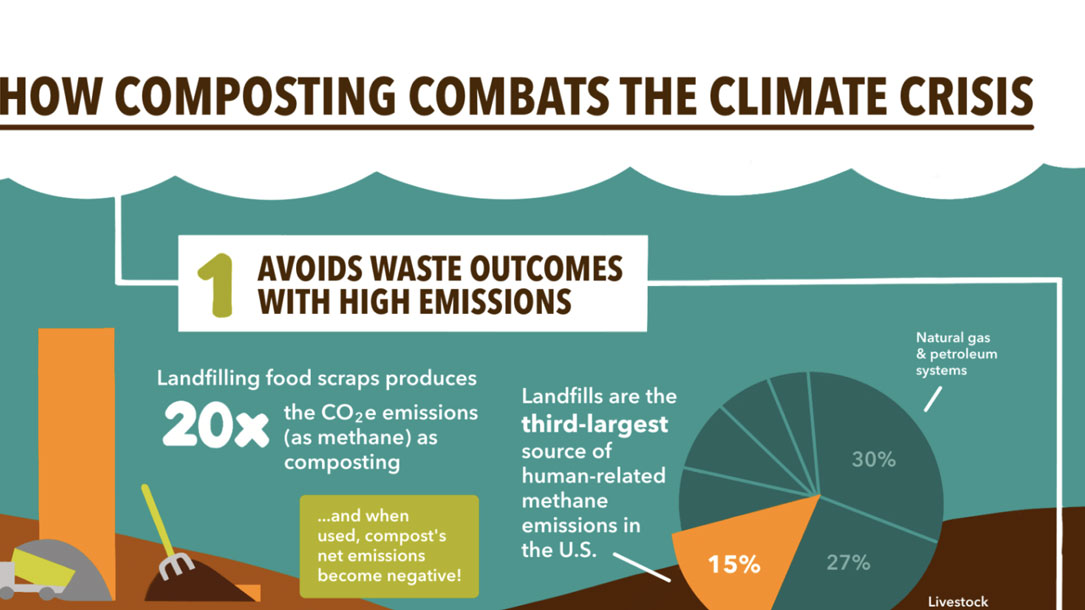
Infographic: How composting combats the climate crisis
Composting cuts greenhouse gas emissions, enhances the ability of soil to act as a carbon sink, and builds community resilience to climate disruptions.
Use our new graphic to share these benefits! It is available for your use (with attribution to the Institute for Local Self-Reliance).

Deep soil inventories reveal that impacts of cover crops and compost on soil carbon sequestration differ in surface and subsurface soils
Increasing soil organic carbon (SOC) via organic inputs is a key strategy for increasing long-term soil C storage and improving the climate change mitigation and adaptation potential of agricultural systems. A long-term trial in California’s Mediterranean climate revealed impacts of management on SOC in maize-tomato and wheat–fallow cropping systems. SOC was measured at the initiation of the experiment and at year 19, at five depth increments down to 2 m, taking into account changes in bulk density. Across the entire 2 m profile, SOC in the wheat–fallow systems did not change with the addition of N fertilizer, winter cover crops (WCC), or irrigation alone and decreased by 5.6% with no inputs.

One simple way to slash methane pollution: composting
In the United States, a staggering one-third of all food — something like 130 billion meals annually — gets thrown out. Each year, that discarded stuff represents an estimated 170 million metric tons of carbon emissions — the equivalent of 42 coal-fired power plants…
According to a new study in the Nature Journal Scientific Reports, composting food scraps results in 38 to 84 percent fewer greenhouse gas emissions than tossing them in landfills…

New research shows practices from the past will be key to future soil carbon solutions
Sometimes to go forward, you must go back.
A new study from Colorado State University’s Department of Soil and Crop Sciences and the Graduate Degree Program in Ecology found that regenerative practices — including integrating crop and livestock systems — were successful as long-term carbon storage solutions.

Regenerative practices successful at long-term carbon storage, study finds
A meta-analysis conducted by Colorado State University researchers found that regenerative agricultural practices are successful as long-term carbon storage solutions. The research considered two different types of soil carbon, particulate organic carbon (POC) and mineral-associated organic carbon (MAOC). Because POC cycles faster in soil, different management for the two types of carbon may help provide better outcomes…

How to make mindsets matter Nat Kendall-Taylor | Nobel Prize Summit 2023
Are you interested in how to talk about science — or conservation information — more effectively?
“Psychological anthropologist Nat Kendall-Taylor presents compelling research about how our ‘cultural mindsets’ are implicit in shaping our thinking and how we consume information. As communicators, we must be mindful of our dominant biases and understand they can impede our trust in science. Watch to learn more about untapped strategies to help us fight against disinformation…”

NSAC’s 2023 Farm Bill Platform
NSAC’s comprehensive 2023 Farm Bill Platform provides title-by-title recommendations across farm bill programs and policies detailing how Congress can better support farmers and ranchers by strengthening their bottom lines, their communities, and their resilience. The platform spans key issue areas including natural resource conservation, local and regional food systems, sustainable agriculture research, structural reform to farm programs, and more, with cross-cutting recommendations, focused on advancing racial equity across farm bill programs, supporting beginning farmers, and addressing the climate crisis and its impacts on our food and farms.
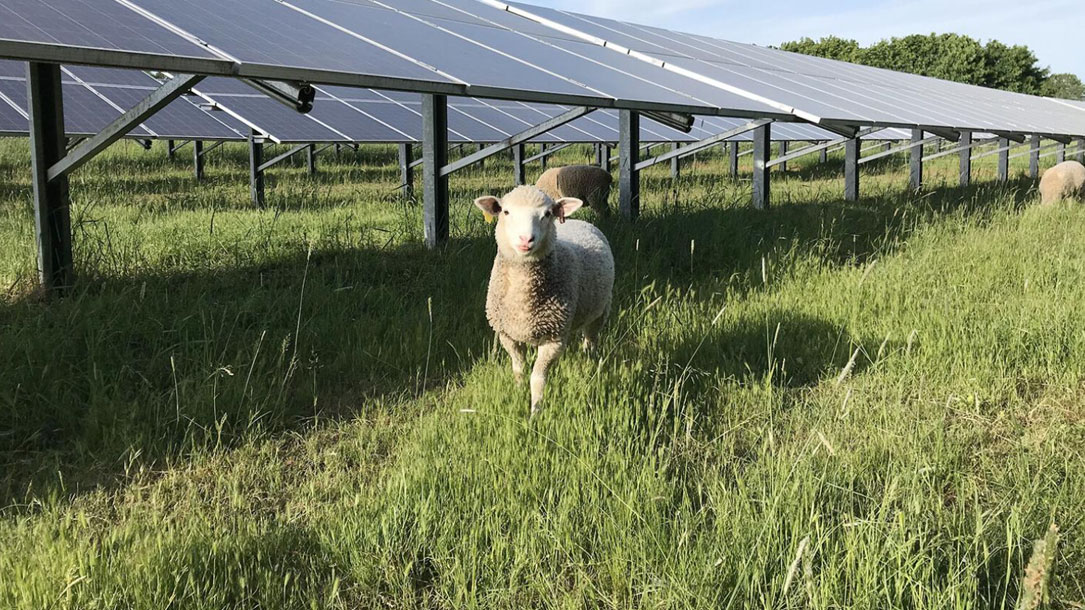

Agrivoltaics bill introduced in U.S. Senate
According to the National Sustainable Agriculture Coalition (NSAC), the study would aim to answer many questions about agrivoltaics, including what panel designs are best for livestock versus crops; what animal breeds are best suited to graze under panels; how to handle fencing, manure, and other livestock considerations in solar panel systems; and how growing crops under panels impacts yields, soil moisture, and other factors.












