Home > Climate News >

Soils could be affected by climate change, impacting water and food
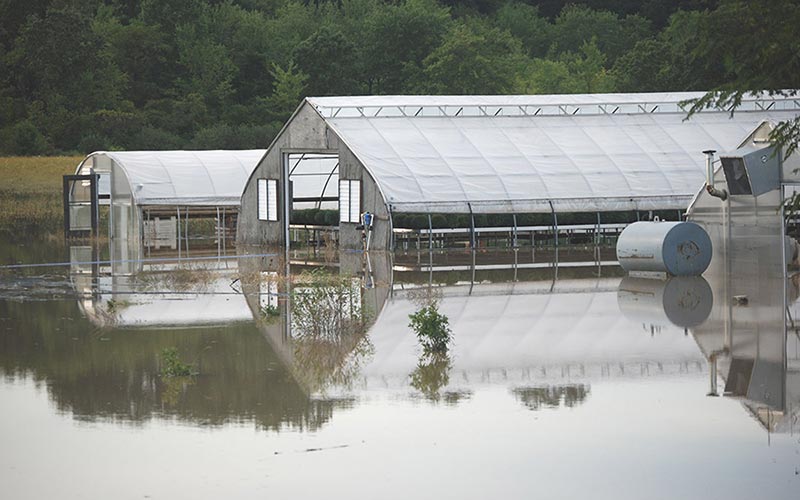
Climate change may reduce the ability of soils to absorb water in many parts of the world, according to a Rutgers-led study. And that could have serious implications for groundwater supplies, food production and security, stormwater runoff, biodiversity and ecosystems…

Oregon State University research shows bright future for agrivoltaics
Oregon is home to more than 37,000 farms across 16 million acres of the state. Our agricultural producers raise animals, supply dairy products, and grow food – and sometimes even generate renewable energy. Wind energy is a good fit in several rural areas of the state where there are strong wind resources and development is compatible with land use and agricultural requirements. While many in the agricultural community have concerns about the ability to farm around solar arrays, for some Oregon farms and ranches, solar development could fit well into their cropping or grazing operations. Such “dual-use development” is subject to rules adopted in 2018 by the Oregon Land Conservation and Development Commission.

Climate warming from managed grasslands cancels the cooling effect of carbon sinks in sparsely grazed and natural grasslands
Grasslands absorb and release carbon dioxide (CO2), emit methane (CH4) from grazing livestock, and emit nitrous oxide (N2O) from soils. Little is known about how the fluxes of these three greenhouse gases, from managed and natural grasslands worldwide, have contributed to past climate change, or the roles of managed pastures versus natural grasslands.

Pollinator deficits, food consumption, and consequences for human health: A modeling study
Animal pollination supports agricultural production for many healthy foods, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and legumes, that provide key nutrients and protect against noncommunicable disease. Today, most crops receive suboptimal pollination because of limited abundance and diversity of pollinating insects. Animal pollinators are currently suffering owing to a host of direct and indirect anthropogenic pressures: land-use change, intensive farming techniques, harmful pesticides, nutritional stress, and climate change, among others.
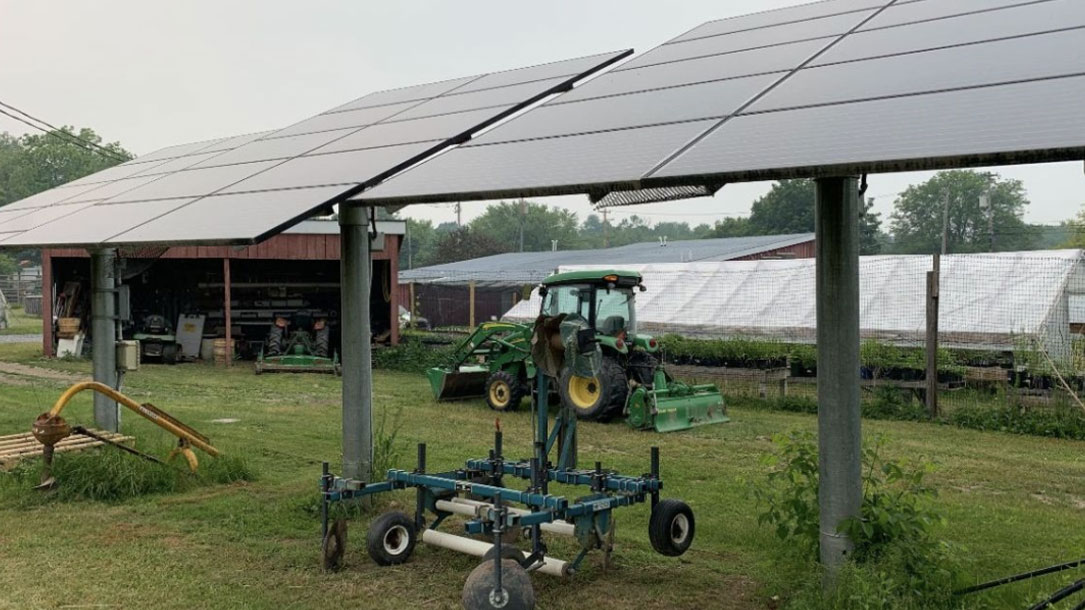

American Farmland Trust applauds introduction of bipartisan bill to advance agrivoltaics
Agrivoltaics refers to the practices of integrating solar energy generation and farming on the same piece of land, which could potentially reduce displacement of agricultural production from farmland as a result of solar development. The concept has been gaining attention in land-constrained countries like Japan and Germany as well as in states like Massachusetts and New Jersey.
“If included in the Farm Bill,” Fink said, “the Agrivoltaics Research and Demonstration Act would secure USDA’s role in advancing this innovation alongside the Department of Energy, AFT, and other partners across the country. Together, we are seeking ways to reduce displacement of farming from productive land as a result of solar energy development.”
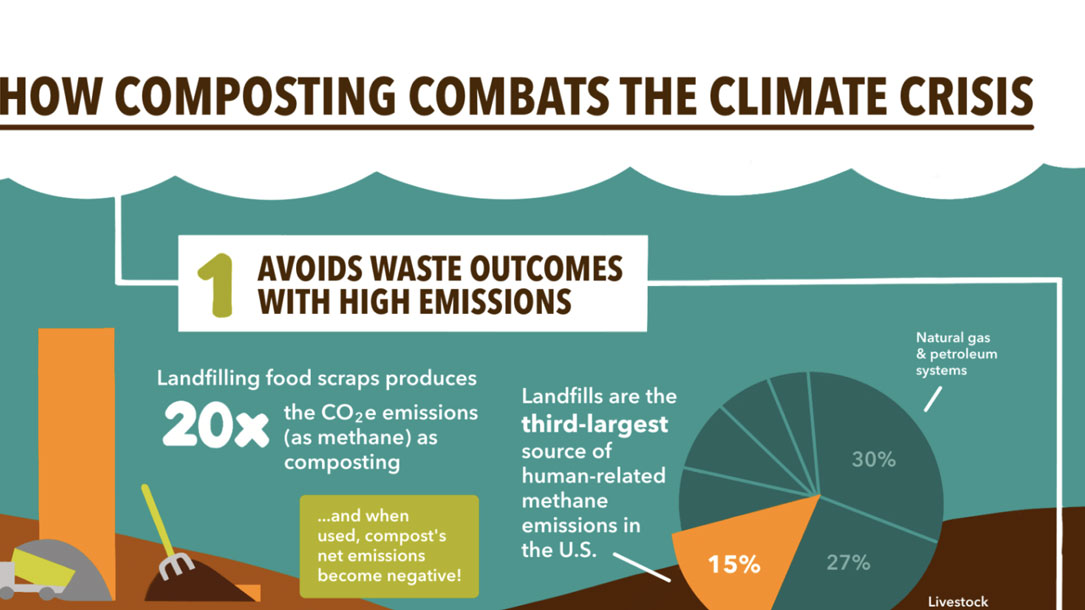
Infographic: How composting combats the climate crisis
Composting cuts greenhouse gas emissions, enhances the ability of soil to act as a carbon sink, and builds community resilience to climate disruptions.
Use our new graphic to share these benefits! It is available for your use (with attribution to the Institute for Local Self-Reliance).

Deep soil inventories reveal that impacts of cover crops and compost on soil carbon sequestration differ in surface and subsurface soils
Increasing soil organic carbon (SOC) via organic inputs is a key strategy for increasing long-term soil C storage and improving the climate change mitigation and adaptation potential of agricultural systems. A long-term trial in California’s Mediterranean climate revealed impacts of management on SOC in maize-tomato and wheat–fallow cropping systems. SOC was measured at the initiation of the experiment and at year 19, at five depth increments down to 2 m, taking into account changes in bulk density. Across the entire 2 m profile, SOC in the wheat–fallow systems did not change with the addition of N fertilizer, winter cover crops (WCC), or irrigation alone and decreased by 5.6% with no inputs.

NSAC’s 2023 Farm Bill Platform
NSAC’s comprehensive 2023 Farm Bill Platform provides title-by-title recommendations across farm bill programs and policies detailing how Congress can better support farmers and ranchers by strengthening their bottom lines, their communities, and their resilience. The platform spans key issue areas including natural resource conservation, local and regional food systems, sustainable agriculture research, structural reform to farm programs, and more, with cross-cutting recommendations, focused on advancing racial equity across farm bill programs, supporting beginning farmers, and addressing the climate crisis and its impacts on our food and farms.

Climate-smart agriculture Inflation Reduction Act Activation Guide
A broad range of companies within the food sector can use IRA-funded agricultural programs to support their climate goals. On average, two-thirds of food sector companies’ emissions are generated by farm-level production, making on-farm sustainability critical for abatement.

Climate change, antibiotics may threaten soil
A study by researchers at the Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies in Millbrook, New York, has shown that when rising temperatures combine with antibiotic residues expelled by livestock, it degrades soil microbe efficiency, soil resilience to future stress, and its ability to trap carbon…












